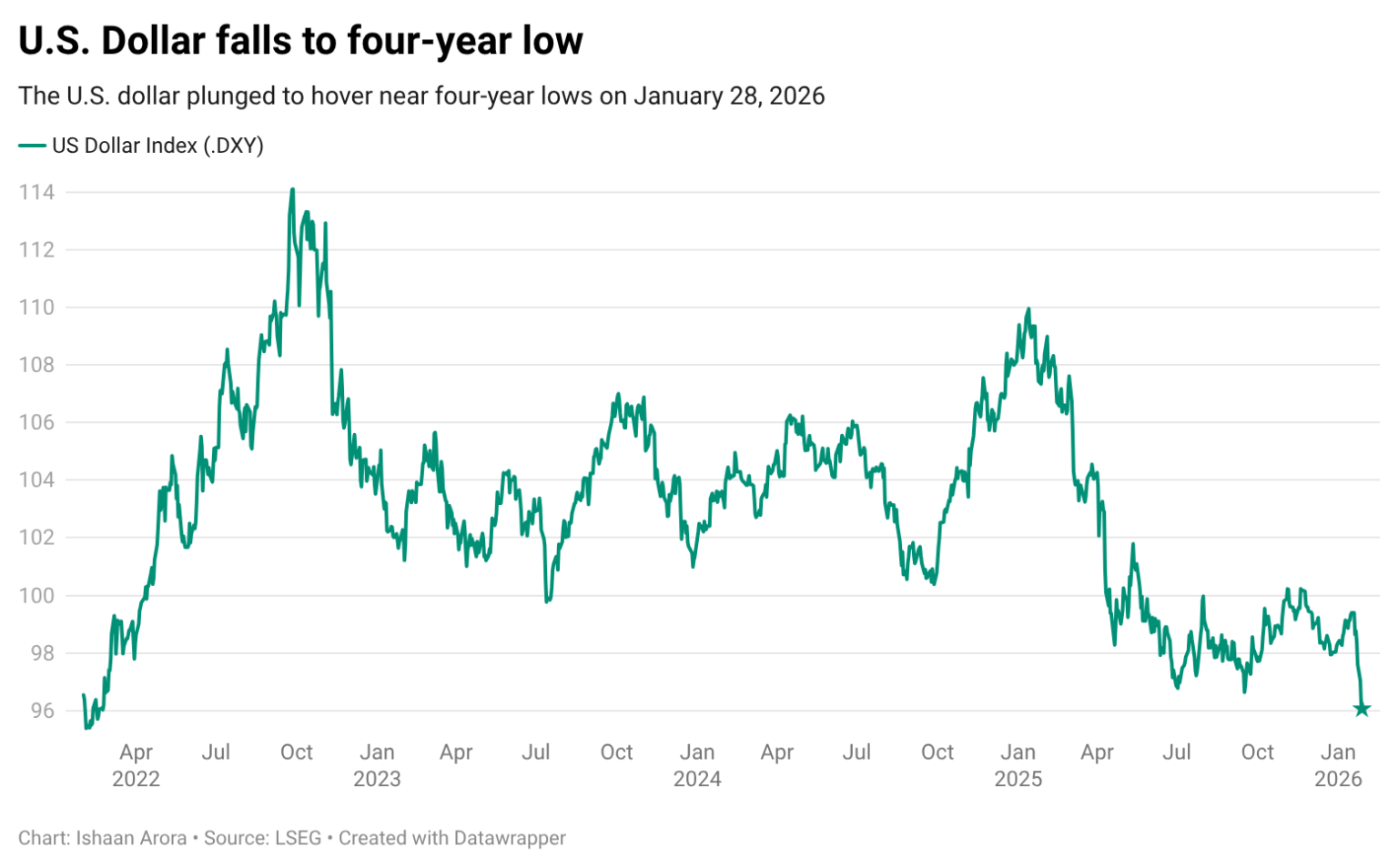
Forging Heat Resistance: Alumina Ceramic Baking Dish Unleashed alumina carbides inc
In sectors where extreme temperatures, chemical direct exposure, and mechanical anxiety merge, normal materials fail while crafted services prosper. The Alumina Ceramic Cooking Meal stands for a course of sophisticated ceramics that goes beyond domestic imagery to come to be a crucial component in high-performance research laboratories, aerospace screening gears, metallurgical processing, and materials research….