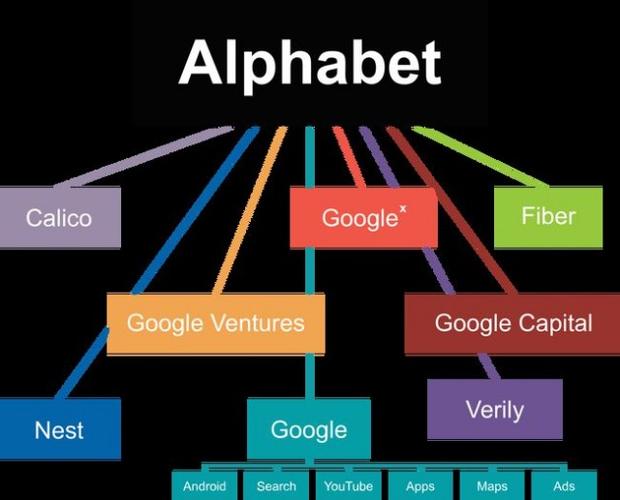
Samsung’s Latest Tablet Can Be Used as a Second Screen for Mac
Samsung has launched its newest tablet, the Galaxy Tab S9. This device now works as a second screen for Mac computers. Users can connect the tablet to their Mac and extend their workspace. The feature is part of Samsung’s new SideSync update. It lets people drag windows from their Mac onto the tablet screen. They…