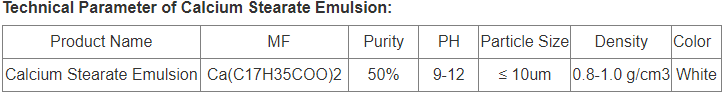
HBN Boron Nitride Ceramics Redefining Advanced Materials boron nitride insulator
In the world of advanced products, where efficiency satisfies precision, couple of compounds have captured the creativity of designers and pioneers rather like HBN Boron Nitride Ceramics. Commonly eclipsed by more acquainted ceramics like silicon carbide or alumina, this exceptional product incorporates the best of both worlds– the structural integrity of ceramics and the distinct…

Boron Nitride Ceramic Discs for Substrates for High Temperature Annealing of Aluminum Scandium Nitride Films
A new development in high-temperature materials processing is gaining attention in the semiconductor industry. Researchers have successfully used boron nitride ceramic discs as substrates for annealing aluminum scandium nitride films. These films are key components in next-generation electronic devices, especially those requiring stability under extreme heat. (Boron Nitride Ceramic Discs for Substrates for High Temperature…

Boron Nitride Ceramic Tubes for Thermocouple Wells in Molten Salt Thermal Energy Storage Systems
A new application for boron nitride ceramic tubes is gaining attention in thermal energy storage systems that use molten salt. These tubes serve as thermocouple wells, protecting temperature sensors in harsh, high-heat environments. Boron nitride offers strong resistance to corrosion and thermal shock, which makes it ideal for long-term use in molten salt baths that…

Boron Nitride Ceramic Crucibles for Evaporation of High Temperature Solders for Vacuum Brazing
A new line of boron nitride ceramic crucibles is now available for high-temperature solder evaporation in vacuum brazing applications. These crucibles are made from high-purity boron nitride, a material known for its excellent thermal stability and resistance to chemical reactions. They can handle extreme heat without breaking down or contaminating the molten metal. (Boron Nitride…

Boron Nitride Ceramic Crucibles for Melting Gallium and Indium Alloys in Compound Semiconductor Production
A new generation of boron nitride ceramic crucibles is now available for melting gallium and indium alloys used in compound semiconductor production. These crucibles offer high thermal stability and excellent resistance to chemical reactions at elevated temperatures. Manufacturers rely on them to maintain purity during critical melting processes. (Boron Nitride Ceramic Crucibles for Melting Gallium…

Advanced Ceramic Coatings for Gas Turbine Blades Improve Oxidation Resistance
A major breakthrough in materials science is helping gas turbine blades last longer and perform better under extreme heat. Researchers have developed advanced ceramic coatings that significantly improve oxidation resistance. These new coatings protect metal components from high-temperature corrosion, a common problem in power generation and aviation engines. (Advanced Ceramic Coatings for Gas Turbine Blades…

Technical Ceramic Coatings for Cutting Tools Extend Tool Life in Metal Machining
A new generation of technical ceramic coatings is helping metal machining operations get more life out of their cutting tools. These advanced coatings are applied to tool surfaces to protect them from heat, wear, and friction during high-speed machining. As a result, tools stay sharper longer and need replacing less often. (Technical Ceramic Coatings for…

Piezoelectric Ceramic Benders Enable Compact and Efficient Micro Positioning Systems
Piezoelectric ceramic benders are now driving advances in micro positioning systems. These components deliver precise motion control in a small package. Engineers value them for their compact size and high efficiency. They convert electrical signals into mechanical movement with great accuracy. This makes them ideal for applications that need fine adjustments. (Piezoelectric Ceramic Benders Enable…

Samsung Announces New Program for Trade-in of Broken Devices
Samsung has launched a new trade-in program that accepts broken devices. The initiative lets customers exchange damaged smartphones, tablets, and other eligible electronics for credit toward new Samsung products. This move aims to make upgrades easier while supporting responsible recycling practices. (Samsung Announces New Program for Trade-in of Broken Devices) The program covers devices with…
Samsung’s Latest Tablet Can Be Used as a Second Screen for Mac
Samsung has launched its newest tablet, the Galaxy Tab S9. This device now works as a second screen for Mac computers. Users can connect the tablet to their Mac and extend their workspace. The feature is part of Samsung’s new SideSync update. It lets people drag windows from their Mac onto the tablet screen. They…